What is Tokennomics? A face-up game with a market maker
What is Tokennomics? What does Tokenomics include and how does it play a role in deciding to invest in a project? Find out here!
Tokenomics - one of the most used concepts when investing in crypto but few understand what it is. A phrase that is easy to understand in theory but very complicated when analyzed in depth.
Therefore, in today's analysis and research, I will help you understand Tokenomics most thoroughly and answer the questions below:
- What are Tokenomics and some of their classifications.
- What role does Tokenomics play in the crypto market in general and DeFi in particular?
- Tokenomics perspective and evaluation method.
- The "structures" inside Tokenomics are complete.
- The role of Tokenomics on project performance.
- Case study of Tokenomics is effective and Tokenomics is not effective.
The article will have a lot of in-depth information, I suggest you can prepare a pen and paper to conveniently note down useful information for yourself.
Disclaimer: This article is written for informational purposes only and is not intended as investment advice.
What is Tokennomics?
Tokenomics is a combination of two words Token and Economics . Therefore, Tokenomics can be seen as the economy of cryptocurrencies, how they are built and applied to the operating model of that project.
Why is Tokenomics important?
Reading this far, you will probably find it quite boring. Token is also just an asset that is traded on an exchange. So what's so special about tokenomics? Before answering this question, let's go through a small quiz to increase the drama!
Take a look at the image below and imagine the crypto market as a multi-party game, including:
- Developer: Andre Cronje, Vitalik Buterin,...?
- Market Maker: CZ Binance, Sam FTX,...?
- Large investment fund: a16z, Multicoin, ParaFi,...?
- Retail investors: Most brothers (including myself).
So who are the people sitting closest to the chessboard, who are the game controllers? Looking at the picture above you will see, even Justin Sun can't access the game, then it is probably the small investors who are standing outside the casino listening to the results of the game.
Who controls the crypto game?
Indeed it is, we are playing a game created by Market Makers, Builders/Developers and large investment funds. From trend of ICO, IEO, IDO to NFT, GameFi on ecosystems.
So what factors will they control the game through? That is the token , the thing that you buy and sell and put your trust in it. But tokens are something built by great developers, builders, and market makers. In short, the crypto market is a zero-sum game, everyone wants to make money, so who will lose?
If you want to make money and understand what Market Maker is doing, you need to understand the operation of the Token, or in other words, it is TOKENOMICS.
We will continue to learn about how the tycoons operate Tokenomics!
Elements of a Token and Tokenomics
This part is quite long, but it will have links and support useful Insights for the following sections, don't miss it. Before diving into the analysis of the application and the value of the token for the project, I will go with you from basic to in-depth, including:
Coin/Token Supply
In the past, Total Supply and Circulating Supply were two frequently used concepts. However, both Coingecko and CoinMarketCap have added a new concept called Max Supply - a concept that is easily confused with Total Supply.
I will explain in detail the 3 concepts of Token Supply and give illustrative examples to make it easier for you to understand in this section.
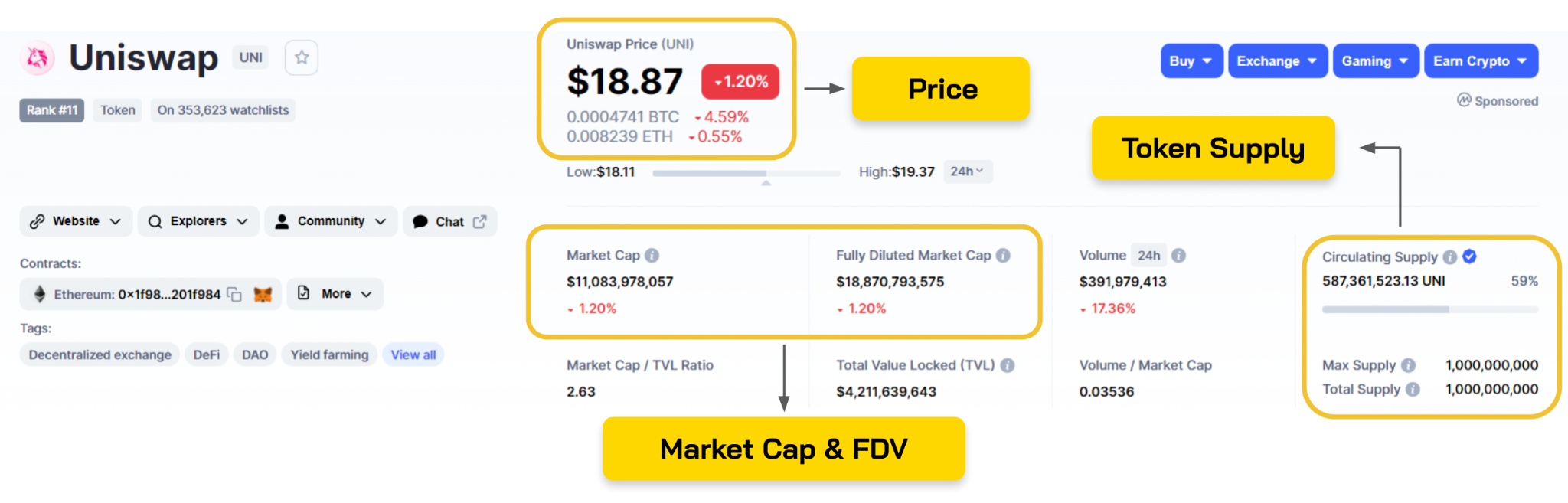
Basic parameters of a coin/token.
1. Total Supply is defined as the total amount of coins/tokens in circulation and locked minus the number of coins/tokens that have been burned. Initially, Total Supply will be a number designed by the project development team to best match the operating model.
In more detail, Total Supply will have the following forms:
- The fixed total supply is the initial predetermined amount of coins/tokens and cannot be changed. Example: Total supply of Bitcoin is 21 million BTC, Total supply of Uniswap is 1 billion UNI,...
- The total supply is not fixed is the amount of coins/token that can change depending on the activity of the project, and is divided into the following groups:
- The total supply increases gradually due to more mining . For example: The amount of ETH in the market will depend on the performance of the Ethereum network, CAKE will be minted when users Farm on Pancakeswap,...
- Total supply decreased gradually due to burn . For example, Binance Coin has an initial total supply of 200 million BNB and is gradually burned to 100 million BNB,...
- The total supply changes continuously due to the Issue-Burn mechanism . For example: Mainly Stablecoins like Algorithmic Stablecoin (FEI, AMPL,...), Crypto-backed Stablecoin (DAI, VAI,...), Centralized Stablecoin (USDT, USDC,...).
2. Circulating Supply is a concept that refers to the amount of tokens being circulated in the market.
3. Max Supply will determine the maximum number of tokens that will exist, including those that will be mined or available in the future.
4. Read Token Supply vị

Read the Token Supply position with 3 different tokens/coins.
Above are the Token Supply parameters of 3 different coins/tokens:
- ETH: Ethereum is a token with no total supply (No Max Supply) and will be minted more when there is a need to use the network. After being minted, ETH will be circulated without being locked by any organization (Circulating Supply = Total Supply).
- SRM: Serum is designed with the largest amount of 10 billion SRM (Max Supply). At the present time, the maximum number of SRMs can reach 161 million SRM (Total Supply), but the actual number of circulation is only 50 million SRM (Circulating Supply).
- NEAR: Near Protocol's Token Supply is the most basic and most common. Total Supply and Initial Design Token Quantity will be equal (Max Supply = Total Supply), gradually unlocked until reaching 1 billion NEAR (Circulating Supply).
Market Cap & Fully Diluted Valuation

Read the Market Cap and FDV position of a token/coin.
Market Cap is the capitalization of the project with the number of tokens circulating in the market at that time. From Circulating Supply, we will calculate the Market Cap.
Market Cap = Circulating Supply * Token Price
Fully Diluted Valuation (FDV) is the capitalization of the project but is calculated with the total number of tokens in circulation and also not yet unlocked of the project. From Total Supply, we will calculate FDV.
FDV = Total Supply * Token Price
Why does capitalization affect growth potential more than price?
Currently, the price of the token depends on many factors, in addition to Fundamental Analysis, it also depends on the Initial Total Supply of the token . Example of a project with token A with a Market Cap of $10,000,000:
- If the project issues 10,000,000 A token ⇒ Each A token = $1.
- If the project issues 10,000,000,000 A token ⇒ Each A token = $0.001.
The number of tokens issued can range from tens of thousands to several billion tokens, but capitalization is an important factor affecting the growth of tokens.
Example : Let Aave and Compound be two projects with equal fundamental analysis potential in the field of Lending. Because of that, Compound can reach Aave's Market Cap.
In terms of price, each COMP costs more than AAVE, but COMP has higher growth potential because Compound has not reached the “ceiling”. If Compound achieved a Market Cap like Aave, each COMP could reach $735.

Misconceptions about price and market cap.
Token Governance
Currently on the market there are about 10,000 coins and tokens. However, not every token follows the Decentralized mechanism like Bitcoin, there will be tokens/coins that are managed according to the Centralized mechanism. I will divide it into 3 basic types:

Token Governance of some coins on the market.
Decentralized (Decentralized Tokens) are coins/tokens whose governance is completely decided by the community and is not pressured to govern by any organization. For example: Bitcoin, Ethereum,...
Centralized (Centralized Token) are coins/tokens whose governance mechanism is decided by a leading organization, they have the power to influence the nature of the coin or project that the token represents. Usually these are Full-backed stablecoin projects like Tether, TrueUSD; exchange tokens like Huobi, FTX, or projects with a Centralized governance model like Ripple,...
From Centralized to Decentralized: There are also coins/tokens built with the initial governance mechanism Centralized, then gradually decentralized to the community.
For example, the original Binance Coin was fully governed by Binance. However, after a while of launching Binance Smart Chain and the “Validator Spotlight” program, Binance has gradually decentralized the network of BSC and BNB tokens for users to control.
Token Allocation
Before investing in a token, Token Allocation will help you know if the distribution of tokens among the stakeholder groups (related groups) is reasonable, as well as their impact on the overall project.

Token allocation of some coin/token on the market.
1. Team
This is the token for the project development team. This will include the amount of tokens of members who contribute value to the project such as founder, developer, marketer, advisor, etc. The ideal number is usually about 20% of the total supply.
- If this ratio is too low, the project team will not be motivated to develop the project in the long term.
- If this ratio is too high, the community will not have an incentive to hold the token of that project, because the token is being dominated by too much of one entity. This causes a number of problems such as concentration of power, the possibility of being overpriced.
2. Foundation Reserve
Reserve is a project's reserve for future product or feature development. This is a token with no specific amount, usually it will account for 20-40% of the total supply.
3. Liquidity Mining
Liquidity Mining is an Allocation that has appeared a lot in recent times, especially after DeFi projects developed strongly from September 2020 until now. Liquidity Mining is a token that is minted as a reward to users who provide liquidity for DeFi protocols.
4. Seed / Private / Public sale
This is the number of tokens for the sale to raise capital for product development. Normally, the project will have three open sales: Seed sale, Private sale and Public sale (details in the Token Sale section).
5. Airdrop / Retroactive
In order for the project to attract initial users, they will often airdrop to users a very small part of the project's token allocation. Usually will account for about 1-2% of the total supply.
Around 2019 and earlier, to receive the Airdrop, users only need to perform a few simple steps such as Like, Follow, Retweet posts on their Twitter page.
However, from 2020, the conditions to receive the Airdrop are much more difficult, requiring users to "skin in the game", use the product to be able to receive the Airdrop or Retroactive. Some typical Retroactives can be mentioned as Uniswap (UNI), 1Inch Network (1INCH),...
Learn: What is an Airdrop? How to participate in Airdrop effectively
6. Other Allocation
Depending on each project, they will have an Allocation section for a specific case, which can be Marketing, Strategic Partnership,... Usually Allocation has a small proportion and can be included in the Foundation Reserve.
The difference between the two cycles:
- 2017-2018: Public Sale accounted for more than 50%, Insider accounted for little. For example: ADA, ETH, XTZ, ATOM,...
- 2019 onwards: Public Sale accounts for 20-30%, Insiders account for the largest proportion. For example: NEAR, AVAX, SOL,...
In there:
- Public Sale is the amount of tokens that are opened for sale to the community.
- Insider includes the development team, investment funds,...
This can be explained because in the past, the project's tokens were not used much in the ecosystem and they needed capital to be able to develop the project. At the present time, the market has had the appearance of large investment funds and tokens that are widely applied in the platform. Therefore, Insider and Foundation will account for a large number of tokens on the market.

The difference in token allocation of coins/tokens founded before 2018 and after 2018. Source: Messari.
Token Release
Token Release is a plan to distribute tokens to the circulating market of a project. Similar to Token Allocation, Token Release greatly affects the price of the token as well as the community's motivation to hold the token. Currently on the market there are 2 types of token allocation:
1. Allocation of tokens according to a predetermined schedule
Each different project will have a different token release schedule, but we can classify it into the following time periods:

Token release of some popular tokens in the market.
Less than 1 year: Projects with a 100% token release rate less than 1 year show that the project team is not a long-term companion to the product they build, and cannot create much value for the platform and the token. there.
From 3 to 5 years: This is the most ideal time to release 100% of tokens, because the crypto market has a very fast rate of change. Since being “Mainstream” in 2017 until now, the crypto market has only experienced a period of 5 years.
In each year, the market has seen the shedding of many ineffective projects and the launch of more potential projects. Therefore, 3-5 years is the ideal number to promote the development motivation of the team, as well as the motivation to hold tokens from the community.
Over 10 years: Except for Bitcoin, projects with a token release schedule of up to 10 years will find it difficult to motivate holders, because they suffer from token inflation for up to 10 years and no one can guarantee that the team will effective during that period.
As such, the number of token releases must be designed to balance the following two factors:
- The rights of token holders when holding tokens of that platform.
- The value of tokens released per day (inflation).
If the number of tokens released is too fast compared to the performance of the project, the token price will tend to decrease because users are not motivated to hold the token.
2. Token allocation according to performance and usage needs
To solve the problem of inflation happening too quickly compared to the original plan. Some projects have chosen to release tokens according to a specific criterion rather than a set time. This is a pretty cool mechanism because it will help stabilize the price of the token if applied properly.
For example, MakerDAO also does not have a specific token replenishment time. Depending on the actual use needs of the platform, the amount of MKR will be allocated appropriately. ⇒ With Lending or Borrowing activities, the new MKR token will be released.
Token Sale
Token sale can be seen as a form of raising capital through the sale of shares similar to companies in the traditional market. However, in the crypto market, shares will be replaced by tokens.
If traditional companies have about 5 fundraising rounds, projects in Crypto will have about 3 token sales to raise capital. Often the valuation of a company will not be specific to each industry, region and size. However, in Series C, large companies can completely value themselves from $ 100 million or more.
- Traditional Company: Pre-seed, Seed, Series A, Series B, Series C.
- Crypto Project: Seed Sale, Private Sale, Public Sale.
For the crypto market, the average valuation will be lower as it is a relatively new market and has a much smaller market cap than the stock markets of some major countries.

The process of coin/token being opened for sale from Seed to Public sale.
1. Seed sale
Seed sale is the first token sale of the project. In this sale, most of the projects have not yet completed the product. There are a number of projects that open to sell tokens as a form of capital raising for deployment.
The funds invested in Seed sale are mostly venture capital funds, they accept high risks but will also be rewarded if the project is successful.
2. Private sale
If the Seed sale is mainly venture capital funds, the Private sale will have the participation of many larger and more famous investment funds. Usually at this stage, projects have launched their products and have partially demonstrated their achievements after raising capital in the Seed sale round.
3. Public sale
Public sale is an open sale of tokens to the community. The project can launch tokens in the form of ICOs like 2017, or launch tokens through third parties in the form of IEOs or IDOs.
4. Fair token distribution
However, there are also many projects that are not open for sale through any form, but will be distributed through activities such as Testnet, Airdrop, Staking, Liquidity Providing,... This helps the project become "average". more equal” to the interested community and reach more users.
Some prominent Fairlaunch Projects can be mentioned as: Uniswap (UNI), Sushiswap (SUSHI), Yearn Finance (YFI),... They do not open token sale in any form to raise funds first, but will distribute. tokens to real users of the platform.
Some pros & cons of this mechanism:
- Advantages: Tokens are distributed to people who contribute value to the project, reducing deep "dump" because Seed sale and Private sale buyers "discharge" tokens.
- Cons: The project "misses" a part of the capital that can be called from the community to develop the project.
5. Impact of Token Sale on Tokenomics
There is no set rule or benchmark for the price difference between token sales. For a project, the Public sale price can be twice the Private Sale price, the Private Sale price can be twice the Seed Sale price. This completely depends on the project.
However, they will keep the spread reasonable. Because if the price difference between each phase is too high, investors who come first will tend to take profits early, on the contrary, investors in the next round will not have the motivation to participate in the sale.
Therefore, projects will apply a token release mechanism to properly distribute benefits among investors. If the price difference of each batch is high, investors who come first have to have a longer lock time. Conversely, investors who buy at a higher price will be able to unlock tokens sooner.
Token Use Case
Token Use Case is the intended use of the token, this is the most important element of a tokenomics that helps you to value a token in the market, based on the benefits that the token brings to the holder.
Currently, FoxCryptoNews Insights has a Series "How It Works - Analysis of Operational Models" to help you analyze the project's operating model as well as analyze the value of the token. You can check out the articles in the series here.

Functions of some tokens/coins on the market.
Normally Token will have the following functions:
1. Staking
Currently, most projects support Staking for their native tokens. This creates an incentive for users to hold tokens because more tokens are distributed as interest. Without the staking mechanism, token holders would suffer from inflation because every day a new number of tokens are minted into circulation.
In addition, Staking also has an additional benefit of helping to reduce the number of tokens circulating in the market, which reduces selling pressure and makes it easier for the price to grow. For networks that use Proof-of-Stake, the increase in the number of staked tokens also makes the network more decentralized and secure.
For example, Cardano (ADA) is growing from $0.2 to $2 (1,000% growth) since the beginning of 2021. Theoretically, to grow like that, the amount of capitalization poured into Cardano must be 10 times.
However, in reality, this is not the case, the capitalization number poured into Cardano is much lower. What makes Cardano grow so strongly is that 75% of Cardano in circulation has been staked, which helps to reduce the selling pressure of ADA in the market, creating momentum for ADA to grow.
2. Liquidity Mining (Farming)
For DeFi tokens, there have been many recent appearances. Users can use them to provide liquidity for DeFi protocols, in return they will be rewarded with the project's native token.
Example: Provide liquidity to Uniswap to get UNI, ...
3. Transaction fee
To make a transaction, users need to pay a fee to the network, more specifically the Validators for them to confirm the transaction for them. Each blockchain network will have its own native token used to pay for the network (usually projects operating in the field of blockchain platform). For example:
- Ethereum uses ETH.
- Binance Smart Chain uses BNB.
- Solana uses SOL.
- Polygon uses MATIC.
4. Governance
In this part I mentioned above, the platforms can be managed under Centralized or Decentralized mechanism depending on the project developer. However, the majority of current DeFi platforms are governed by a Decentralized mechanism.
This means token holders will be able to propose and vote to make changes to the platform they participate in. Proposals can be related to transaction fees, token release speed, or larger issues such as proposals for the project development team to expand to the new blockchain.
Currently, prominent DeFi platforms such as Uniswap, Sushiswap, Compound, etc. have all applied the Decentralized Governance mechanism allowing users to participate in governance. However, most of the community only stops at Voting power, but cannot create Proposal for the platform, because the amount of tokens needed to create Proposal is often very high value.
5. Other benefits (Launchpad,...)
This is one of the important factors that helps the token to be circulated and creates a great incentive for users to hold the token. Regular Launchpad projects will require users to stake tokens in order to participate in the sale. Or have the right to participate in the NFT prize draw,...
For example: Polkastarter requires holding POLS, DAO Maker requires holding DAOS,...
Case study on Tokenomics
Disclaimer: This is my personal opinion and should not be considered investment advice of any kind.
Note: To evaluate a project with growth potential or not, Tokenomics is an important factor, however, the price of the token as well as the potential of the project is also evaluated through many other factors. Tokenomics is not the only factor affecting the potential for price growth.
Below I will mention some projects with effective and ineffective tokenomics so that you can easily visualize.
Effective Tokenomics
1. Binance Coin (BNB)
Token Supply
- Initial total supply: 200,000,000 BNB.
- Unlock time: 5 years (100% unlocked).
- Includes burn mechanism until Circulating Supply is 100,000,000 BNB.
⇒ Help deflate, create momentum to increase prices and create motivation to hold for BNB holders.
Token Use Case
However, this is not the main reason for BNB's outstanding growth recently. The brightest point for BNB is the design of token use cases that allow BNB to be fully applied on the Binance exchange and the Binance Smart Chain network.
- Binance Exchange : Reduced transaction fees, Join Launchpad, Staking, Mortgage & Loan, Derivatives Trading,...
- Binance Smart Chain : Network Fees, Main Currency, Staking, Farming (BNB is used as the main asset to create liquidity pairs, similar to ETH in Ethereum system and this is the main factor that makes BNB buy demand increase. strong growth).
Currently, Binance is planning to develop Binance Pay, and BNB can completely become a popular payment unit at any time if it is successfully applied by Binance. BNB's success has been reflected in its outstanding growth this year.
Result: BNB grew in a $20 accumulation range to peak around $650 (+3,250%) and is holding at $300 (+1,500%).

The coin burning mechanism reduces the supply of BNB.
2. Pancakeswap (CAKE)
CAKE is the native token of the AMM DEX Pancakeswap platform on the Binance Smart Chain ecosystem.
Token Supply
- CAKE has no total supply (No limit of CAKE).
- 530,000 CAKE are distributed every day through Syrup Pool, Farming Pool and Lottery Pool.
- CAKE will be burned when the user uses ANY Pancakeswap product.
Token Use Case
CAKE is designed for comprehensive application in Pancakeswap products, including Syrup Pool (Staking), Staking to participate in IFO, Lottery and Prediction Payment Instruments.
⇒ Although there is no total supply, Pancakeswap very well controls the circulating supply of CAKE, helping to control the balance between Token Release and Token Burn. Pancakeswap has been very skillful in increasing the application of CAKE tokens in the platform to create Buy Demand for CAKE, as well as maintain Incentive for CAKE holders. Therefore, CAKE has had a very strong growth since its launch.
Result: CAKE grew from $0.4 to a peak of $40 (+10,000%) and is holding steady at $14 (+3,500%).
Learn more: PancakeSwap Performance Model Analysis

CAKE is fully applied to all products in Pancakeswap.
Tokenomics doesn't work
Pangolin (PNG)
PNG is the token used in the AMM DEX Pangolin of the Avalanche network. Although it has a similar function to CAKE in AMM DEX such as providing liquidity for the exchange,... but from my personal perspective, Pangolin has tokenomics with many problems and does not work effectively.
Token Supply is not reasonable
The first thing is that PNG has a total supply of 538,000,000 PNG, every 4 years the number of PNGs distributed to the market will be halved. This is the same mechanism as Bitcoin, which makes the total time for PNG to be unlocked up to 36 years.
However, Bitcoin is a trusted asset by the community, and PNG is a very new token, there is no guarantee that Pangolin's team will be active to develop the product during that 36 year period, not yet. The age of the crypto market is just over 10 years old.
Unable to balance Revenue and Token Release Value
The second thing, at the moment Pangolin is unlocking 175,000 PNG/day (valued at $197,500/day). But Pangolin's sales are less than $30,000 a day. This makes PNG holders no longer motivated to hold the project's tokens because they do not receive the benefits they deserve.
Therefore, when investing in a token, you need to have a multi-dimensional perspective. The project side can "draw" many scenarios when achieving achievements, but you need to verify with actual data. Will the revenue of that project achieve as expected or not?
⇒ Unreasonable in Token Release Schedule, cannot apply PNG in Pangolin platform. The “perspective” of tokenomics does not match the actual figures.
Result: After peaking at $15, PNG has dropped to its current price of about $1.2/PNG (12x split). Even when the market grew strongly around April - May 2021, PNG price growth was very weak.
In this September, the tokens of the Avalanche system have also grown very strongly such as AVAX, SNOB, XAVA, ... but PNG still has a very slow growth rate. Despite being an AMM backed by Avax Labs, Pangolin has also fallen short of Trader Joe's.
Learn more: Pangolin Performance Pattern Analysis

Pangolin's unreasonable Tokenomics leaves users with no incentive to hold PNGs.
Case Study Perspective
As I analyzed above, how to design tokenomics will not be constrained by any factors. Depending on the operating model and market that the project is targeting, the team will have a way to design the tokenomics appropriately.
When evaluating a tokenomics, you must not only evaluate their application, but also analyze the market that the project is targeting.
Is the market the project is targeting large-scale, has many users, is such a design of tokenomics balanced between applicability for the project and benefits for token holders?
For example, Pancakeswap (CAKE), from the beginning they identified the active market as the Binance Smart Chain ecosystem - the ecosystem with the 2nd largest DeFi TVL in the market and already has a large user base.
Therefore, they will design Tokenomics for Liquidity Mining Reward to attract a large number of Users from the very beginning. Then, to increase the buy demand for CAKE, the Pancakeswap team increased the applicability of CAKE in all Pancakeswap features.
summary
In the above article, I have analyzed specifically to help you understand the structure and role of a tokenomics in the market. Here are some important Recaps:
- Tokenomics is a collection of many internal factors such as Token Supply, Token Application, Token Sale, Token Release,...
- Tokenomics is an important factor but cannot be separated from the operating model to accurately assess the effectiveness and growth of the token.
- Tokenomics can be "varied" with many different designs. But let's focus on the platform's revenue and how the project captures value for the token (can be found in the Activity Model Analysis articles).
Oct 03, 2022
























