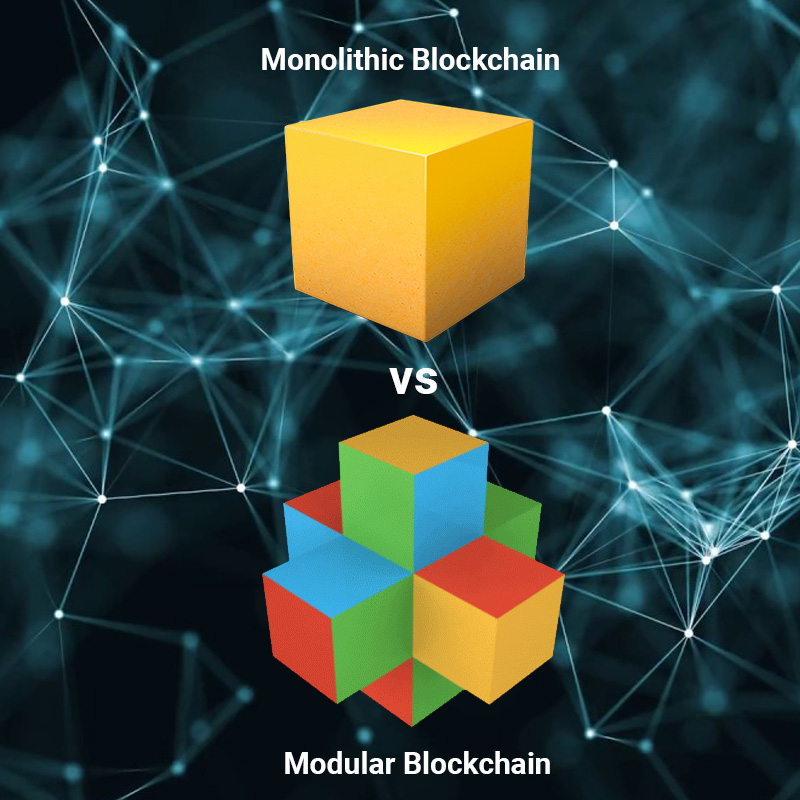
What is Monolithic Blockchain and Modular Blockchain?
The Merge is getting closer and closer, the whole world is looking at Ethereum. You are probably very familiar with keywords like Ethereum 2.0, The Merge… However, this transformation of Ethereum also marks an important development step for Modular Blockchain – a new direction for platform projects. foundation. So, What is Monolithic and Modular Blockchain? Find out with me below!
The Core Nature of Blockchain
To better clarify how Monolithic Blockchain and Modular Blockchain work, we will learn the core concepts together:
1/ Consensus (Consensus) ):Consensus algorithms are simply mechanisms used in distributed computer systems to reach agreement on a single data value or network state between machines. in the system.
For the traditional way of data management, assuming the data of a university student (personal information, test scores, etc.), only the administrator has the right to edit and authorize the data. affect the data. In contrast, blockchains will decentralized operate, allow self-regulating and updating data without depending on a third party. They involve the contributions of hundreds of thousands of participants working on verifying and validating transactions that occur on the blockchain and on block mining operations.
To achieve the aforementioned decentralization, blockchain needs an efficient, fair, reliable, and secure mechanism to ensure that transactions occur on the blockchain are authenticated and recognized by all parties. This is the job of the consensus mechanism.
2/ Data Availability:Data availability is the assurance that the block proposer has published all transaction data for a block and whether the transaction is available to other participants. Ethereum transactions are processed in blocks. These blocks are linked together to form a “blockchain”.
Data availability is important because from a blockchain point of view, if we can't reproduce something with the data we have available, it won't exist.
3/ Execution (Execution):It is the nodes that perform transactions and thereby maintain and develop the state of the blockchain. You can simply understand the execution of pending transactions.
Learn about Monolithic Blockchain
What is Monolithic Blockchain?

Monolithic Blockchain is a blockchain built to implement all three core components of the blockchain in the same space (Layer-1). To do this, the monolithic blockchain is optimized for consensus, block space or execution (depending on what the project is aiming for).
Example:
When a blockchain aims to generate higher throughput, it is built towards increasing block space and tries to process and store more transactions in the same block. This will force nodes that want to join the network to have hardware/software that meets the requirements => barriers for nodes => fewer nodes join the network => less decentralized.
In addition, reducing the number of nodes will make transaction processing go through fewer nodes => Faster transaction processing speed. However, then the project needs to trade off the decentralization and security.
Monolithic Blockchain Working Mechanism
Monolithic Blockchain works according to the consensus protocol established for the blockchain. To participate, you need to run a node that matches the requirements set by the network. The best example is Ethereum, any user who wants to run their own node needs to first define the type of node they want to run. After setting it up, they download blockchain data from the network. After this process, they begin to join the network following the protocol rules.
– Advantages of Monolithic Blockchain:The biggest advantage of this type of blockchain is that if it maintains security and safety, it will reach decentralization, thereby helping users easily use applications of blockchain technology.
– disadvantage of Monolithic Blockchain:Because it is designed to process 3 core components simultaneously, blockchain in this form can only optimally handle 2/3 of the components and must accept compromise/sacrifice the rest.
- If a blockchain is decentralized, it is safe. But in order to maintain security, it cannot be scalable and thus provide lower throughput.
- If a blockchain is scalable and decentralized, it is likely not secure because there will be barriers to validators.
- If a blockchain is scalable and secure, it probably shouldn't be decentralized.

From the above analysis, you can see that the entire monolithic blockchain is stuck in a certain problem, and it will be difficult for them to fully solve all three of the above. So a number of third-party support solutions have emerged, most notably Ethereum's Layer-2 solutions or Ethereum's attempt to switch from PoW to PoS.
- See also: All about The Merge of Ethereum
Monolithic Blockchain has shown that solving the problem is extremely difficult. So, the idea of creating a blockchain that can "split" the implementation of the three core components mentioned above appeared: Modular Blockchain.
Learn about Modular Blockchain
What is Modular Blockchain?
The most important feature of Modular Blockchain is that they split the aforementioned three tasks instead of doing them all at once on Layer-1.
The idea is to make the system more efficient by making the block space larger, narrowing the validators (nodes) to focus on shards, and thus increasing the throughput of the blockchain by multiple.
In summary, it can be said that all the limitations of a Monolithic Blockchain are effectively transferred on the Modular Blockchain. Let's go deeper with us to see how Modular Blockchain does this.
1/ Execution: For Modular Blockchain, not only Layer-1 participates in transaction processing but there will be a split between Layer-1 and Rollups.
Rollups act as an additional layer to Layer-1. They will operate on the assumption that they do not change the underlying infrastructure of Layer-1 (i.e. do not guarantee the security of transactions), but only process transactions, then send them back. Layer-1. A validator on Layer-1 will confirm and allow the transaction to be added to the blockchain.
Rollup allows to reduce the burden on Layer-1, increase throughput for the blockchain by "compressing" transactions and processing separately.
2/ Data Availability: Modular Blockchain uses Sharding to scale the blockchain exponentially without compromising security and decentralization.
Sharding Technology

The core idea of Sharding is as follows: Assume that you have a proof of PoS chain with a large number (e.g. 10000) validators and you have a large number (e.g. 100) blocks that need to be verified. . No computer is powerful enough to validate all these blocks before the next set of blocks appears.
Therefore, they need to split the verification work in a random way. specifically, they will randomly shuffle the validator node list, then assign the first 100 validators in the (shuffled) list to verify the first block, the second 100 will verify the 2nd block…
Thus, a random group of validators will be chosen to verify a given block. This random set of validators is referred to by the term “committee”.
When each validator validates a block, they will output a signature to confirm they have done it. Thus, now the whole job will be to validate 10000 signatures instead of validating 100 blocks (the workload is greatly reduced).
At this point, if you double the power of the validator node => authentication is added 2 times total signature => blockchain can reduce the number of deposits and increase the validator node by 2 times (both reducing the barrier to validator node and increasing the number of validator nodes) => the project is more decentralized and decentralized, and the overall power is increased up to 4 times.
At this point, you might be wondering, is sharding essentially splitting a blockchain into 100 small blockchains? In fact, creating 100 commits is completely different from splitting into 100 small blockchains.
First, committed is a random set, thereby limiting network attacks. Next, sharding allows that if something goes wrong leading to a damaged shard, it doesn't affect the entire chain (because it's parallel), so it can be restored more easily.
3/ Consensus:Modular Blockchain will work under the Proof-of-Stake mechanism, because PoS will help and strengthen the modular blockchain.
In Proof-of-Work (PoW), the security of the network depends on the computing hardware that miners use. The more complex the hardware, the more likely it is to solve cryptographic calculations, thus helping the blockchain to survive.
In proof-of-stake, however, security is an element of the economic capital that users decide to lock (or bind) to the network.
Now, in the former case, you need expensive hardware (which will become obsolete over time and need to be upgraded). However, in the second case, you only need to create a button (it can be very easy to set up) and deposit the minimum required capital to participate in the staking process. Thus, PoS makes it significantly easier for a larger set of validators to participate in network consensus. Modular Blockchain Example
Ethereum 2.0 with the transition to PoS and the application of Sharding technology is the best example of Modular Blockchain. In addition, you can focus on Celestia and Fuel Network, which are also new projects that are expected to work on Modular Blockchain.
Thus, the advantage of Modular Blockchain is that it offers a new direction to solve the three problems of the traditional blockchain, better meeting the needs of scalability, decentralization and security in the growing crypto landscape. mass-adoption. However, Modular Blockchain also has certain problems such as:
- Most of the projects are in the process of construction, still need a lot of time to test.
- The compatibility of Modular Blockchain with existing DApps as well as technological barriers to building other DApps on Modular Blockchain.
Summary
In the first part, we learned about Modular Blockchain and Monolithic Blockchain together. Surely you also see the advantages and superiority of Modular Blockchain. In the next part, I will analyze a few typical projects that are pursuing Modular Blockchain for you to have more diverse perspectives. See you guys in the next posts.
Sep 13, 2022


-400-400.webp)