What is Blockchain Consensus Algorithm?
The blockchain algorithm is an integral part of the blockchain. Not only play a role in keeping the network secure, these algorithms also help blockchains ensure decentralization in the way they operate.
Surely anyone who learns about the crypto market knows that Bitcoin has a consensus algorithm called Proof of Work, the same coin with the second largest market capitalization of Ethereum before. So why here Ethereum will have to make The Merge 2.0 move completely to Proof of Stake.
So what is the blockchain algorithm? What types of algorithms are there? What kind of algorithms do blockchains currently use? What is the difference between the mechanics of this consensus algorithm? Let's learn about the types of concurrency algorithms in today's article.
Core knowledge:
- The blockchain's consensus algorithm is the mechanism that ensures the transactions created on the blockchain are correct, honest, and transparent.
- Blockchains need a consensus algorithm because this is the mechanism for creating and maintaining the network's peer-to-peer decentralization.
- There are many types of blockchain algorithms today, the most popular of which is Proof of Stake.
What is Blockchain Consensus Algorithm?
The blockchain's consensus algorithm is the mechanism that ensures the transactions created on the blockchain are correct, honest, and transparent. In essence, blockchain consists of many nodes that combine to create a network. In order for a transaction to be recorded on the blockchain, it must be agreed upon by all nodes on the network simultaneously.
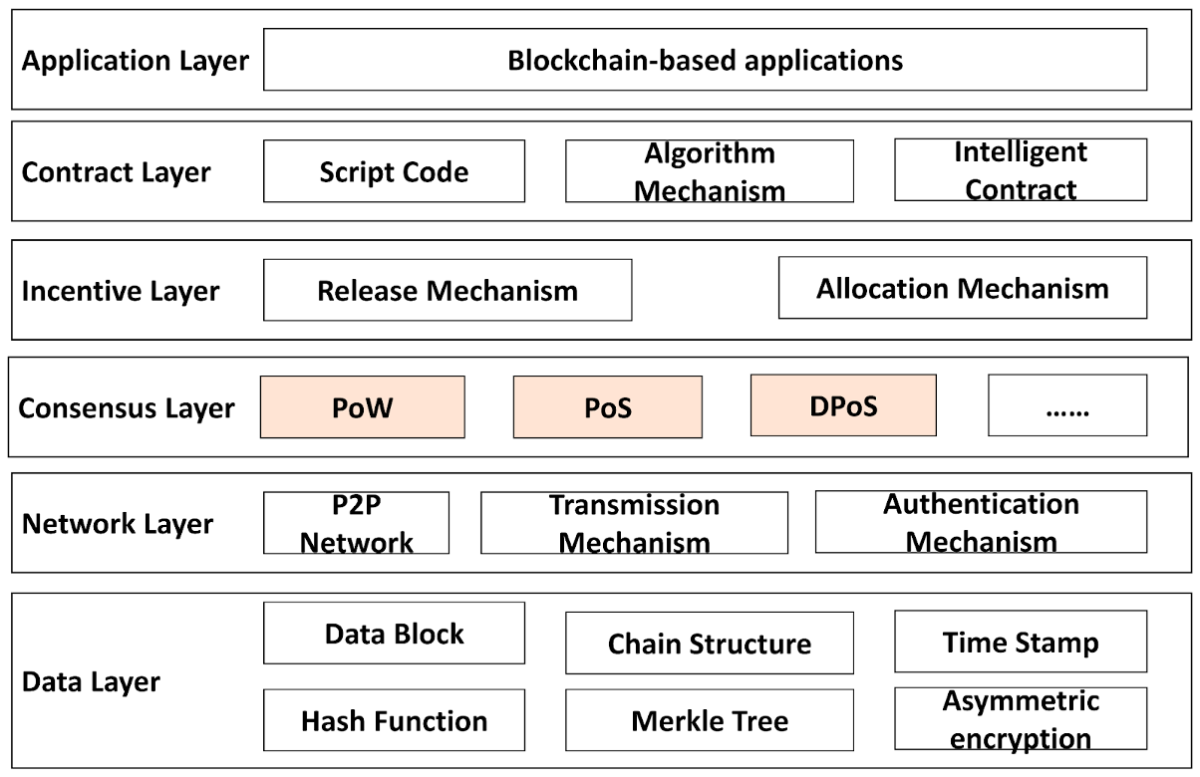
If a block in the network is changed, this data is compared with the data of other blocks. If there is a difference then it will not allow that data to be written inside the Blockchain. That's how blockchain is designed to resist data change.
The consensus algorithm is also an integral part of a blockchain, playing a core role in keeping blockchains decentralized and secure. In the beginning, Bitcoin's Proof of Work consensus mechanism was the main choice of developers, but now, there are many different consensus mechanisms. Among them, the most popular is Proof of Stake.
To understand more about the structure and operation of Blockchain, you can refer to the article below.
Learn: What is Blockchain Technology?
Why does a blockchain need a consensus algorithm?
A blockchain must always have a consensus algorithm, why is that?
Blockchains need a consensus algorithm because this is the mechanism for creating and maintaining the network's peer-to-peer decentralization. Instead of a few individuals or organizations controlling the entire system, blockchain allows anyone to join the network by becoming a node.
The consensus mechanism is also a solid protection layer of the blockchain against data changes as well as against fraudulent transactions by hackers, thanks to the consensus mechanism, a transaction will always be verified by the nodes in the network. network in a peer-to-peer manner.
If the consensus mechanisms are always stable, solid, and secure, no one party will be able to exploit or attack the blockchain. The more nodes/validators there are, the more secure and decentralized that blockchain becomes. This means that Bitcoin and Ethereum are the two most secure blockchains to date.

Popular Blockchain Consensus Algorithms

Proof of Work
Proof of Work is the first blockchain consensus algorithm born, this algorithm is used by Bitcoin - the world's first cryptocurrency.
Proof of Work (PoW) aka proof of work. With this consensus mechanism, nodes will use computing power to solve problems that generate hashes. The first node that solves the problem, wins the right to validate the transaction, and then receives a reward of BTC. This process is called “mining” , where nodes act as miners.
When a node solves the problem and confirms the transaction, that transaction is also checked and confirmed by all other nodes in the network. If the answer is passed, all nodes will add this transaction to the blockchain, making the blockchain easy to verify and synchronize.
Because of the use of computing power to secure the blockchain, Proof of Work requires a large amount of electricity consumption as well as expensive costs for the required hardware.
In addition, a block on a Proof of Work blockchain also takes longer to be generated and validated, which makes the algorithm less efficient and resource-intensive (even environmentally unfriendly). than other consensus algorithms.
This is the first consensus mechanism and is tied to Bitcoin (BTC) , Ethereum (ETH) ,...

Proof of Stake
Proof of Stake (PoS), aka proof of stake, is the most popular algorithmic consensus mechanism today, first used by Ethereum. Instead of using computer power, Proof of Stake requires nodes participating in validating transactions to stake a certain amount of the blockchain's native token in order to gain the right to participate in validation and block generation.
Usually blockchains that use Proof of Stake will require a minimum number of tokens to participate as validators.
For example, to become a validator of Ethereum, users will have to stake at least 32 ETH (about 33 thousand USD at the time of writing). These tokens are staked to ensure that the nodes work well, i.e. if the node is offline for too long or commits fraud, the staked tokens may be partially or completely lost depending on the level of the token. .
Validator nodes in the Proof of Stake network will receive transaction fees as a reward. When a transaction takes place, validators will be randomly selected to validate the transaction, the more tokens staked, the percentage chosen will increase accordingly.
With the above operations, Proof of Stake is a more cost-effective, environment-friendly algorithm than Proof of Work. To become a validator node is also simpler and does not have to use too "terrible" hardware devices.

Proof of Stake is considered superior to Proof Of Work and is very popular with many blockchains in use such as Cosmos (ATOM) , Binance Coin (BNB) , Ontology (ONT) , ...
Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS)
Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) , aka delegated proof of stake, is an evolved version of Proof of Stake.
Instead of choosing a random validator like PoS, token holders will choose a number of professional nodes for these nodes to operate the network, in return, token holders will share a reward for the work of maintaining security for the network. In each block, the number of delegators chosen to validate transactions is limited and random.
In addition, Delegated Proof of Stake has a limited number of validators, usually ranging from 10 to 100, compared to the original PoS, DPoS is considered to be faster and has better performance.
DPoS helps to ensure honesty and fairness by implementing continuous voting activities and also continuous shuffling in the system, to ensure that those selected are honest and accountable.
Some projects using this mechanism are: Cosmos (ATOM), EOS (EOS) , Tron (TRX) ...

Proof of History (PoH)
Proof of History , aka proof of history, is a fairly new consensus algorithm introduced by Solana . Instead of following logic, PoH uses the transaction timeline as a reference. So, validator nodes of the Solana network can generate subsequent blocks without having to coordinate with the entire network.
Basically, Proof of History does not compute output from input data, instead PoH uses a feature to use pre-existing outputs as inputs. This mechanism is built to solve the problem of timing in decentralized networks where the same timeline is not available.
Proof of Authority (PoA)
Proof of Authority , aka proof of authority, is a consensus algorithm based on reputation. Unlike PoS, the validators responsible for validating blocks will not be selected based on the number of coins they hold, but will be based on their own reputation.
The network's number of validators is limited, making Proof of Authority a scalable model. In which, transactions are validated by selected and approved validators, who are also system regulators.

PoA values identity, that is, those selected are trusted validators, which makes it possible for some companies and businesses to apply this algorithm. Not only that, the PoA algorithm can be considered as a valuable option for applications in the logistics and supply chain industries.
To have the above advantages, PoA has to trade off with decentralization, sacrificing decentralization in exchange for performance and scalability, in other words, this model only makes centralized systems more efficient. should be more efficient.
PoA was first proposed by former Ethereum CTO, Gavin Wood in 2017, then used by Binance Smart Chain (BNB Chain) and other exchange chains like HECO, OKExChain, Gatechain, Cronos, etc.
Proof of Contribution (PoC)
Proof of Contribution monitors the actions of all validators in the network and ranks those validators according to their contributions - a mechanism quite similar to the social credit system. A user's reputation is assessed based on the number of tokens staked and historical transactions.
Before joining the network, users will have to stake an amount called a security deposit. After completing the computations, nodes with validated results will be rewarded with transaction fees and staked tokens from nodes that do not have correct results.
Proof of Reputation (PoR)
Proof of Reputation, is an upgraded version of Proof of Contribution. The operation process of PoR is similar to that of PoC, the difference is in the choice of validator. While anyone can become a node of a PoC blockchain, PoR requires a more rigorous selection process.
To be a validator on the PoR blockchain, a user's reputation must be so great that having fraudulent activities on the blockchain can instantly destroy the reputation.
Therefore, the network's validators are usually companies. This is a relatively abstract concept because most companies participating in the system if cheating will affect their reputation, large companies will suffer more.
A typical project using the PoR algorithm is GoChain Coin (GO) .
Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT)
Byzantine Fault Tolerance (or Byzantine Fault Tolerance System - BFT) is a system that can solve the Byzantine problem. This means that the BFT system can continue to function even if some nodes fail or take actions that harm the general network.
This algorithm allows verifiers to manage each state of a chain, while also sharing messages with another chain, for accurate transaction records and assurance of fidelity.
Some projects using this algorithm: NEO (NEO) , Ripple (XRP) , Stellar (XLM) ...
Other consensus algorithms
Currently, there are many different consensus mechanisms, serving both public and private needs. There are a few other names that can be mentioned such as Proof of Location (PoL), Proof of Burn (PoB), Proof of Zero (PoZ), Proof of Weight (PoWeight), Direct Acyclic Graph Tangle (DAG),...
These blockchain algorithms are quite difficult to change, so people often think of creating a new mechanism. Newer blockchains with newer consensus mechanisms will lead to the continued development of blockchain in the future.
Summary
The consensus algorithm is an integral part of the blockchain. With continuous development, in the future there may be more superior algorithms, meeting the higher needs of users, which may also replace the current uniqueness of Proof of Stake. Don't forget new types of algorithms will always be updated on FoxCryptoNews Insights channels!
Oct 07, 2022













