What is Arbitrage? Risks of arbitrage in Crypto
Arbitrage is one of the highly profitable tactics but requires users to have knowledge of crypto as well as a little knowledge of programming languages to be able to maximize profits.
In the crypto market, we sometimes see a few investors boasting huge profits from arbitrage trades. However, arbitrage is harder than it seems. These are good investors who seize opportunities and know how to make the most of them.
To avoid being FOMO. Let's demystify what arbitrage is and how it works in this article.
What is Arbitrage?
Arbitrage is arbitrage, i.e. buying and selling of the same asset on different markets to profit by taking advantage of the difference in the price of the asset itself. This can happen on any financial market like crypto, stocks, commodities, fiat currencies, etc.
Applying this definition to the crypto market, it can be understood that crypto arbitrage refers to arbitrage trading with crypto assets, which is a strategy of buying and selling crypto between different markets and profits generated from trading. That asset has different prices on different exchanges.
An easy example is when a convenience store owner buys cheaper bread at a nearby store and then sells them in his store at a higher price. The owner of the shop was essentially doing arbitrage on two different markets (his shop and the one nearby).
The profit from arbitrage also depends on the trading volume. It may be insignificant on a small scale, but the potential profit of arbitrage is very high on a large scale. Therefore, arbitrage is a form of trading with low risk but high return for investors with the ability to detect and execute.
Arbitrage trading is the result of liquidity and data fragmentation. For now, arbitrage settlement remains a major challenge for market makers. In other words, the profit from arbitrage is increasing, especially with the advent of decentralized finance ( DeFi ).
How Arbitrage Works in Crypto
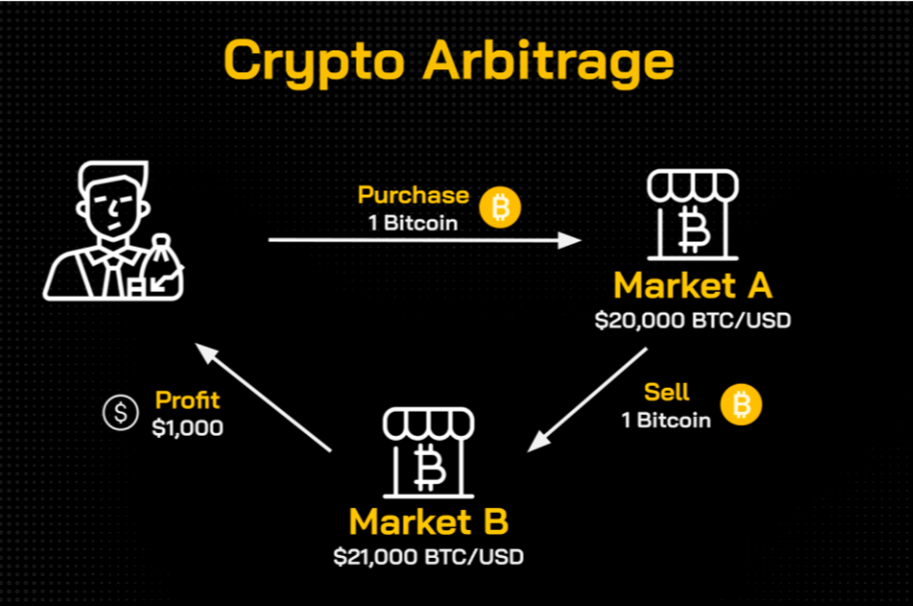
For traders, the goal of arbitrage is simply to profit from buying an asset at a certain price and then selling it at a higher price. Here is a simple example of how profitable arbitrage works:
- Suppose a trader A realizes that there is a difference in the price of Bitcoin in 2 markets (crypto exchanges).
- Trader A buys 1 Bitcoin for $20,000 on exchange X.
- Then transfer my 1 Bitcoin to another market (exchange Y), the price of Bitcoin at exchange Y at that time was 21,000 USD.
- Thanks to the $1,000 price difference, he makes $1,000 in profit from selling 1 BTC for $21,000.
- If the transaction fee is included, the profit will be less than 1,000 USD.
In fact, traders often take advantage of fragmented liquidity on DEXs on different blockchains to trade arbitrage, which can require more complex asset swaps. If the trader has miscalculated, arbitrage can result in loss.
In addition to being a tool for traders to make profits, arbitrage also plays a role in increasing market liquidity, as a bridge to keep asset prices stable across different markets.
Arbitrage classification in crypto
Exchange arbitrage
Arbitrage trading on crypto exchanges ( CEX ) is the most basic way to approach this trading method. Traders only need to buy assets on one exchange, then sell them on another exchange, the higher the price difference, the higher the profit will be.

With the advent of DeFi, traders have more options by arbitrage trading through DEXs. Arbitrage via DEX helps traders avoid the management risk of centralized exchanges, providing more arbitrage opportunities due to fragmented liquidity.
With DeFi, traders can use more complementary tools for arbitrage such as bridge, flash-loan , mem-pool transaction ... To optimize these tools, traders need to have a lot of experience and have to handle a lot of operations. .
However, arbitrage across DEXs also has disadvantages. Transaction speed on DEX exchanges depends on blockchain speed, in the case of Ethereum, blocktime is about 15 seconds, the time it takes to conduct a transaction can affect price and profit. In addition, the MEV mechanism can cause traders to be front-run, with DEXs having low liquidity, slippage can cause traders to suffer losses.
Spatial arbitrage
Exchanges are usually located in different countries, users only have limited access to some exchanges depending on nationality. For example, the Coinbase exchange regulates access to users in accordance with the laws of the United States. So spatial arbitrage exists to compensate for the gap between different regions.
Sam Bankman-Fried (SBF), the crypto billionaire known as the founder of FTX, is one of the prominent examples of spatial arbitrage. Previously, Sam noticed the disparity between Bitcoin prices at South Korean and US exchanges, also known as Kimchi Premium. Not only Korea, Japan is also a market where Sam realized there was a price difference, with a difference of 10% Sam has earned millions of dollars in arbitrage profits.
Spatial arbitrage exists because of different countries' views on crypto. Localized cryptocurrency exchanges, decentralized exchanges (DEXs) can solve this problem. However, DEXs also create many arbitrage opportunities for crypto traders.
Funding rate arbitrage
Funding rate bridges the gap between the perpetual contract price and the actual value of the asset. Perpetual traders pay mutual fees when trading, depending on whether the position they are opening is long or short.
Simply put, if the funding rate is positive, it means that traders who open long positions will pay fees for the short and vice versa. Traders can simultaneously open 2 opposite positions with the same volume to receive funding fees.

For example, a trader can open a short position of 10,000 USD and buy 10,000 USD worth of spot asset on the exchange. As such, the trader is not exposed to the risk of price fluctuations, and receives a profit from the funding fee if the funding rate is positive.
The profit from funding rate arbitrage depends on the funding fee rate and position volume.
Risks of arbitrage
Transaction fee
In the process of arbitrage trading, traders will have to bear a lot of different fees, such as transaction fees, withdrawal fees, gas fees, etc. This accumulated over time can exceed the amount of profit earned. Okay.
Traders can solve this problem by choosing platforms, exchanges with low trading fees, or optimizing trades with high volume can also reduce transaction fees.
Time difference
Traders need to be extremely careful in timing arbitrage because buying and selling occur simultaneously in a short period of time. The market with both retail and institutional investors engaged in arbitrage can cause high price slippage.
Risks of bots
Traders who want to make high profits with arbitrage need to trade with high frequency and extremely precise time, that's why professional investors often use bots to trade. However, the trading bots can also encounter errors and do not work as expected, leading to loss of investment, the programming of trading bots is also quite complicated.
Traders who do not use bots will have a much more difficult time than traders with arbitrage bots. However, in order to code to be arbitrage bot requires traders to have certain knowledge of programming languages.
Security
Because arbitrage trading requires a lot of capital and is divided into many different platforms and markets, it is impossible to avoid the risk of asset division. In addition, hacking and rug-pull are also common risks in the crypto market. Therefore, it is recommended to use large reputable exchanges and reputable DEXs for arbitrage trading.
Frequently asked questions about crypto arbitrage
Is Arbitrage Good for the Crypto Market?
The arbitrage activities of traders make the market more efficient, asset prices are kept stable in different markets. The arbitrage trader is also an integral part of the market.
Should arbitrage bots be used?
With arbitrage transactions that need millisecond accuracy and continuous transaction processing, using bots for arbitrage will bring many advantages to traders. However, bots are not necessarily profitable, users need to have programming knowledge and can consider between coding themselves and buying bots.
How profitable can arbitrage trading be?
An example of profitable arbitrage in the crypto market.
Arbitrage can be considered as a form of low-risk trading, the profit on each arbitrage trade is usually small because the spread is usually low. A trade with a spread of about 10% is very rare, mostly at a few percent, except in exceptional cases. However, each trade can be executed quickly, traders can make many trades per day, resulting in significant cumulative profits.
Summary
Arbitrage trading in the crypto market is known to be one of the ways to make huge profits, but it is quite difficult to do manually and requires a lot of knowledge, so it is not for the majority of users. Currently, arbitrage opportunities are increasingly competitive due to increasingly advanced bots.
Oct 11, 2022













