What is Gas Price & Gas Limit? Tips to optimize Gas Fee when trading
Gas Fee is the fee to be paid to make a transaction. So what is Gas Price and Gas Limit? How will the transaction fee per Blockchain be different?
It can be said that the thing that causes the most headaches for you when trading is the gas fee. The gas fee is too high or unreasonable can affect your profit a lot.
Even sometimes wanting to do retroactive or interact with smart contracts also makes you hesitate or ignore if the fees are too high, especially on Ethereum, where it is called leaving a lot of tears for traders when pressing their stomachs. accept high fees for making transactions.
So what is gas fee? What is Gas price & Gas limit? How are they different? Brothers and I find the answer through the gas fee analysis article below.
What is Gas Fee?
Gas Fee (or Gas fee) is a type of transaction fee that you have to pay for a transaction to be made, in which, gas is a unit of measurement for the computer energy needed to perform a specific transaction on the Internet. network.
If you normally ride a motorbike, you have to fill up with gas to run, then in blockchain transactions too, you must have gas for the network to perform transactions.
In the picture below, you can observe the execution of a transaction that goes through many computational steps of the computer, each of which requires gas to proceed.
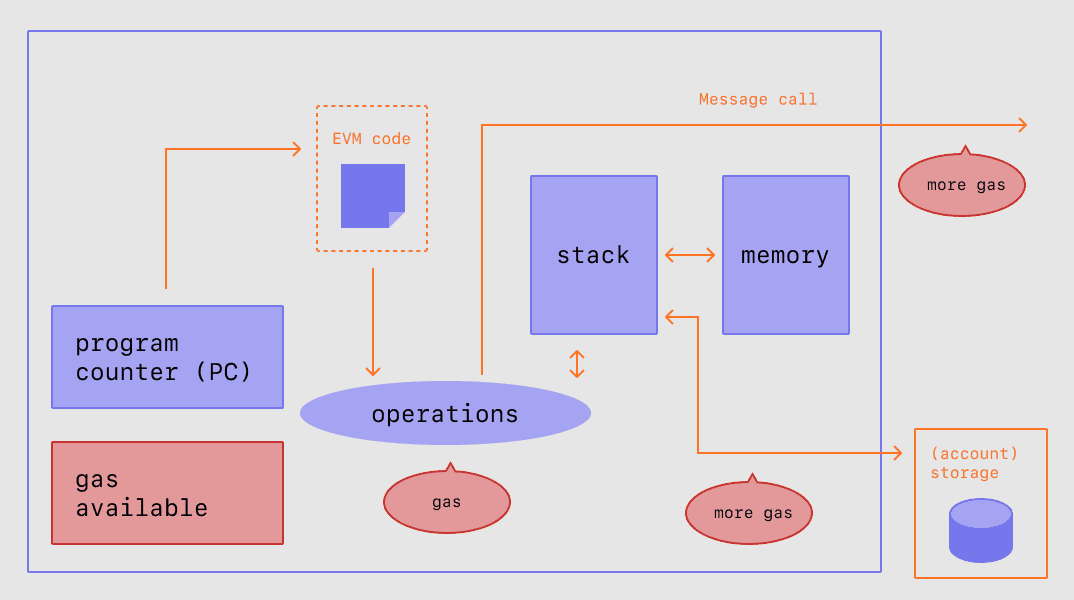
Thus, Gas will be used to:
- Exchange completed.
- Execution of smart contracts.
- Launching decentralized applications (dApps)
- Payment for data storage.
For example, in reality, if you want to run 10km, you need to pour 0.5 liters of gasoline and pay 9000 VND. Similar in blockchain and crypto, if you want to make a transaction to transfer 1000 ETH to another wallet on the Ethereum network, you need some gas to conduct the transaction ⇒ This gas will be converted into ETH for you to pay.
Differentiate Gas Limit and Gas Price
The structure of Gas Fee will include 2 parts:
What is Gas Limit?
Gas Limit is the maximum amount of gas a user is willing to pay to perform an operation or confirm a transaction. The default value of the Gas Limit varies depending on the time and type of transaction. User is allowed to set Gas Limit.
The need for a Gas Limit to complete a transaction depends on the complexity of the transaction. The more complex the transaction, the more computational resources it consumes, and therefore the more gas it consumes.
What is Gas Price?
Gas Price is the amount in the native coin of that blockchain that users are willing to spend per unit of Gas.
Gas Price will affect the speed of confirmation of transactions by miners/validators in the network and include them in new blocks.
- The higher the Gas Price a user is willing to pay ⇒ The higher the reward of the miner/validator ⇒ The faster the Miner/Validator will confirm your transaction.
- Conversely, the lower the Gas Price that users are willing to pay ⇒ Users will have to wait longer. If you are not in a hurry, you can save money by setting a lower Gas Price.
The Ethereum blockchain alone will calculate Gas Price in units of Gwei, Gwei itself is a denomination of ETH - each Gwei equals 0.00000001 ETH (10-9 ETH).
Example: Instead of saying Gas Fee is 0.00000001 ETH, you can say Gas Fee is 1 Gwei. Currently, Ethereum is the blockchain platform that attracts a large number of Dapps to build and develop on it. DeFi players must definitely understand Ethereum and Ethereum's gas fee to catch the trend in time.
Suppose when trading, Gas Limit Ethereum is 21,000 and Gas Price is 106 Gwei. So:
Gas Fee = 21,000 x 106 Gwei = 2.226,000 Gwei ~ 0.002226 ETH
It means you are willing to pay 0.002226 ETH for the transaction to go through.
Gas Fees on Blockchains
Transaction on any Blockchain, pay Gas Fee in coins of that blockchain. This means that depending on different blockchain platforms, Gas fees are also calculated in different units.
In other words, when you make a transaction or want to transfer tokens on any blockchain, you will use the original coin of that blockchain to pay the transaction fee.
Gas Fee in each blockchain is completely different. If you want to transact on any blockchain, you must make sure you have the original coin of that blockchain as Gas. Specifically:
- Want to trade on Ethereum: Buy, sell, store ERC20 tokens like ETH, USDT ERC20,.... ⇒ Pay Gas Fee in Ether (ETH).
- Want to transact on Solana: Buy, sell, store SPL tokens like SRM, RAY, etc. ⇒ Pay Gas Fee in Solana (SOL).
- Want to trade on Binance Smart Chain: Buy, sell, store BEP20 tokens,… ⇒ Pay Gas Fee with Binance Coin (BNB).
If you are still wondering which coin to use as a transaction fee (Gas Fee) when using which blockchain, you can see in the picture below:

Note:
- Father Token: The coin you use as the Gas Fee corresponding to the blockchain.
- Child Token: Is the token standard supported on the respective blockchains.
Why is Gas Fee required?
With the appearance of Gas Fee:
- Limit network spam, increase network security.
- Increased performance when implementing transaction processing algorithms. Developers will have to try to limit the number of steps needed when making a transaction to save costs.
- Pays for efforts and compensates for the amount of computing power used by miners.

Tips to save Gas Fee when swapping on AMM
Currently, there are a lot of AMMs for you to use and trade the coins you want such as:
- Pancakeswap on BSC;
- SerumSwap, LunaDEX on Solana;
- Uniswap, Sushiswap on Ethereum;
- MDEX on Heco Chain.
To simplify transactions on AMMs for you, FoxCryptoNews Wallet has integrated all 9 AMMs mentioned above into Coin98 Wallet App, along with the transaction fee optimization mechanism, Coin98 Wallet as a solution to help you experience The trading process is economical and fast.

In addition, you can also apply the following tips to save gas fees:
- Optimize transaction steps, as few steps as possible. Because every step, you will have to spend gas to increase the gas fee.
- Anticipate the amount of gas to avoid the lack of gas causing the transaction to fail and incur additional fees. Use Scan websites to refer to transaction fees and choose when gas is cheap to conduct transactions. Typical: EtherScan for Ethereum, BSCscan for Binance Smart Chain,.....
- Monitor the network's transaction density to avoid network congestion, high gas fees and the risk of transaction failure. For example: Before trading on Ethereum, you can check the transaction density information on https://ethereumprice.org/gas/ .
In addition to Gas Fee, there is another concept that you may also encounter in the transaction process, which is Gas War, you can learn more at: What is Gas War? How to win the Gas War?
Conclusion
Gas Fee is your eternal concern when entering the Crypto world, hopefully this article has helped you better understand it and have more tips to make your experience with Gas Fee less tiring. more tired.
Oct 17, 2022














